Types of matches
Cricket is a multi-faceted sport with multiple formats, varying playing standard and level of formality and the desired time that the match should last. A pertinent division in terms of professional cricket is between matches limited by time in which the teams have two innings apiece, and those limited by number of overs, in which they have a single innings each. The former, known as first-class cricket, has a duration of three to five days (there have been examples of "timeless" matches too); the latter, known as limited overs cricket because each team bowls a limit of typically 50 or 20 overs, has a planned duration of one day only (a match can be extended if necessary due to bad weather, etc.).Typically, two-innings matches have at least six hours of playing time each day. Limited overs matches often last six hours or more. There are usually formal intervals on each day for lunch and tea with brief informal breaks for drinks. There is also a short interval between innings.
Amateur cricketers rarely play matches that last longer than a single day; these may loosely be divided into declaration matches, in which a specified maximum time or number of overs is assigned to the game in total and the teams swap roles only when the batting team is either completely dismissed or declares; and limited overs matches, in which a specified maximum number of overs is assigned for each team's innings individually. These will vary in length between 30 and 60 overs per side at the weekend and the ever popular 20 over format during the evenings. Other forms of cricket, such as indoor cricket and garden cricket remain popular.
Historically, a form of cricket known as single wicket had been extremely successful and many of these contests in the 18th and 19th centuries qualify as major cricket matches. In this form, although each team may have from one to six players, there is only one batsman at a time and he must face every delivery bowled while his innings lasts. Single wicket has rarely been played since limited overs cricket began.
Test cricket
Main article: Test cricket
A Test match between South Africa and England in January 2005. The men wearing black trousers are the umpires. Teams in Test cricket, first-class cricket and club cricket wear traditional white uniforms and use red cricket balls.
Although the term "Test match" was not coined until much later, Test cricket is deemed to have begun with two matches between Australia and England in the 1876–77 Australian season. Subsequently, eight other national teams have achieved Test status: South Africa (1889), West Indies (1928), New Zealand (1929), India (1932), Pakistan (1952), Sri Lanka (1982), Zimbabwe (1992) and Bangladesh (2000). Zimbabwe suspended its Test status in 2006 due to its inability to compete against other Test teams,[48] and returned in 2011.[49]
Welsh players are eligible to play for England, which is in effect an England and Wales team. The West Indies team comprises players from numerous states in the Caribbean, notably Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, Trinidad & Tobago, the Leeward Islands and the Windward Islands.
Test matches between two teams are usually played in a group of matches called a "series". Matches last up to five days and a series normally consists of three to five matches. Test matches that are not finished within the allotted time are drawn. In the case of Test and first-class cricket: the possibility of a draw often encourages a team that is batting last and well behind to bat defensively, giving up any faint chance at a win to avoid a loss.[50]
Since 1882, most Test series between England and Australia have been played for a trophy known as The Ashes. Some other bilateral series have individual trophies too: for example, the Wisden Trophy is contested by England and West Indies; the Frank Worrell Trophy by Australia and West Indies and the Border-Gavaskar Trophy between India and Australia.
Limited overs
Main article: Limited overs cricket
See also: One Day International and Twenty20 International
Sir Viv Richards of the West Indies was voted by Wisden as the greatest One Day International batsman of all time.
Twenty20 is a new variant of limited overs itself with the purpose being to complete the match within about three hours, usually in an evening session. The original idea, when the concept was introduced in England in 2003, was to provide workers with an evening entertainment. It was commercially successful and has been adopted internationally. The inaugural Twenty20 World Championship was held in 2007 and won by India, three subsequent events have been held which were won by Pakistan, England and West Indies respectively. The next tournament is scheduled to be held in 2014. After the inaugural ICC World Twenty20 many domestic Twenty20 leagues were born. First of them was Indian Cricket League which was a rebel league since it was not authorized by BCCI. BCCI then formed its official league called the Indian Premier League. The official league went on to become a successful annual affair that attracted players and audience around the globe, while the Indian Cricket League has been disbanded. After the success of Indian premier league many other domestic leagues were formed in all major cricketing nations. Recently Twenty20 Champions League was formed as a tournament for domestic clubs of various countries.In this league competition played between the top domestic teams from major cricketing nations.
National championships
Main article: First-class cricket
Yorkshire County Cricket Club in 1895. The team first became County Championship champions in 1893.
Australia established its national first-class championship in 1892–93 when the Sheffield Shield was introduced. In Australia, the first-class teams represent the various states. New South Wales has won the maximum number of titles with 45 to 2008.
National championship trophies to be established elsewhere included the Ranji Trophy (India), Plunket Shield (New Zealand), Currie Cup (South Africa) and Shell Shield (West Indies). Some of these competitions have been updated and renamed in recent years.
Domestic limited overs competitions began with England's Gillette Cup knockout in 1963. Countries usually stage seasonal limited overs competitions in both knockout and league format. In recent years, national Twenty20 competitions have been introduced, usually in knockout form though some incorporate mini-leagues.
Club cricket
A typical club cricket match in England.
Club cricket is frequently organised in a league or cup format. Games are limited by either time or overs. Limited overs games usually last between 20 and 60 overs per innings. A less common, but more traditional, format is limiting the game by time only. Games can range from a few hours in the evening to two days long. A modern innovation is the introduction of Twenty20 competitions, both as a format in the existing leagues and new leagues solely based on Twenty20, such as LastManStanding.
Standards of play can vary from semi-professional to occasional recreational level and club cricket is often enjoyed as much for the social element as for the competition. Most clubs have their own ground to play on regularly, often including a field and pavilion or club house. An exception being 'Wandering Sides' who use other's grounds.
Many leagues have been formed around the world of varying degrees of professionalism, the oldest being the Birmingham & District Premier League in the Birmingham area of England, founded in 1888.
Other types of matches
Main article: Forms of cricket
A game of French cricket in progress in Jervis Bay, Australia
Indoor Cricket was first invented in 1970.[51] It is similar to outdoor cricket except that is played in an indoor sports hall with 6 players per team. It is extremely popular in the UK with national championships and multiple independent leagues. Another less formal version of indoor cricket is played in a smaller arena with a soft ball and without pads was invented some years later and is commonly played in the Southern Hemisphere, and even has its own nominal international championships, including World Cups.
In the UK, garden cricket is a popular version of the sport, played in gardens and on recreation grounds around the country by adults and children alike. Although a cricket bat and ball are generally used, other equipment such as pads and gloves are not. The exact rules will vary based on the number of participants and the available space.
Families and teenagers play backyard cricket or tennis ball cricket in suburban yards or driveways, and the cities of India and Pakistan play host to countless games of "Gully Cricket" or "tape ball" in their long narrow streets. Sometimes the rules are improvised: e.g. it may be agreed that fielders can catch the ball with one hand after one bounce and claim a wicket; or if only a few people are available then everyone may field while the players take it in turns to bat and bowl. Tennis balls and homemade bats are often used, and a variety of objects may serve as wickets: for example, the batter's legs as in French cricket, which did not in fact originate in France, and is usually played by small children.
In Kwik cricket, the bowler does not have to wait for the batsman to be ready before a delivery, leading to a faster, more exhausting game designed to appeal to children, which is often used in physical education lessons at UK schools. Another modification to increase the pace of the game is the "Tip and Run", "Tipity" Run, "Tipsy Run" or "Tippy-Go" rule, in which the batter must run when the ball touches the bat, even if it the contact is unintentional or minor. This rule, seen only in impromptu games, speeds the match up by removing the batsman's right to block the ball.
In Samoa a form of cricket called Kilikiti is played in which hockey stick-shaped bats are used. In original English cricket, the hockey stick shape was replaced by the modern straight bat in the 1760s after bowlers began to pitch the ball instead of rolling or skimming it. In Estonia, teams gather over the winter for the annual Ice Cricket tournament. The game juxtaposes the normal summer pursuit with harsh, wintry conditions. Rules are otherwise similar to those for the six-a-side game.
International structure
Main articles: International structure of cricket, International Cricket Council and World Cricket League
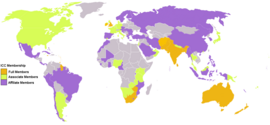
ICC
member nations. The (highest level) Test playing nations are shown in
orange; the associate member nations are shown in yellow; the affiliate
member nations are shown in purple.
The ICC has 104 members: 10 Full Members that play official Test matches, 34 Associate Members, and 60 Affiliate Members.[52] The ICC is responsible for the organisation and governance of cricket's major international tournaments, notably the Cricket World Cup. It also appoints the umpires and referees that officiate at all sanctioned Test matches, One Day International and Twenty20 Internationals. Each nation has a national cricket board which regulates cricket matches played in its country. The cricket board also selects the national squad and organises home and away tours for the national team. In the West Indies these matters are addressed by the West Indies Cricket Board which consists of members appointed by four national boards and two multi-national boards.
Members
Main article: List of International Cricket Council members
Full Members
Full Members are the governing bodies for cricket in a country or associated countries. Full Members may also represent a geographical area. All Full Members have a right to send one representative team to play official Test matches. Also, all Full Member nations are automatically qualified to play ODIs and Twenty20 Internationals.[53] West Indies cricket team does not represent one country instead an amalgamation of over 20 countries from the Caribbean. The English Cricket team represents both England and Wales.| Nation | Governing body | Member since[53] | Current Test rankings | Current ODI rankings | Current T20 rankings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cricket Australia | 15 July 1909 | 2 | 1 | 5 | |
| Bangladesh Cricket Board | 26 June 2000 | 9 | 9 | 10 | |
| England and Wales Cricket Board | 15 July 1909 | 3 | 5 | 8 | |
| Board of Control for Cricket in India | 31 May 1926 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| New Zealand Cricket | 31 May 1926 | 5 | 7 | 6 | |
| Pakistan Cricket Board | 28 July 1953 | 4 | 6 | 3 | |
| Cricket South Africa | 15 July 1909A | 1 | 4 | 4 | |
| Sri Lanka Cricket | 21 July 1981 | 6 | 3 | 2 | |
| West Indies Cricket Board | 31 May 1926 | 8 | 8 | 7 | |
| Zimbabwe Cricket | 6 July 1992 | 10 | 10 | 9 |
Top Associate and Affiliate Members
All the associate and affiliate members are not qualified to play Test Cricket, however ICC grants One Day International status to its associate and affiliate members based on their success in the World Cricket League. The top six teams will be awarded One day international and Twenty20 International status, which will allow the associate and affiliate teams to be eligible to play the full members and play official ODI cricket.The associate and affiliate teams who currently hold ODI and T20I status:
| Nation | Governing body | Member since | Current ODI rankings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan Cricket Board | 2001[54] | 14 | |
| Cricket Canada | 1968[53] | 16 | |
| Cricket Ireland | 1993[53] | 11 | |
| Cricket Kenya | 1981[53] | 13 | |
| Koninklijke Nederlandse Cricket Bond | 1966[53] | 12 | |
| Cricket Scotland | 1994[53] | 15 |
Statistics
Main article: Cricket statistics
Organized cricket lends itself to statistics to a greater degree than
many other sports. Each play is discrete and has a relatively small
number of possible outcomes. At the professional level, statistics for
Test cricket, one-day internationals, and first-class cricket are
recorded separately. However, since Test matches are a form of
first-class cricket, a player's first-class statistics will include his
Test match statistics – but not vice versa. The Guide to Cricketers was a cricket annual edited by Fred Lillywhite between 1849 and his death in 1866. Wisden Cricketers' Almanack was founded in 1864 by the English cricketer John Wisden (1826–1884) as a competitor to The Guide to Cricketers. Its annual publication has continued uninterrupted to the present day, making it the longest running sports annual in history.Certain traditional statistics are familiar to most cricket fans. The basic batting statistics include:
- Innings (I): The number of innings in which the batsman actually batted.
- Not outs (NO): The number of times the batsman was not out at the conclusion of an innings they batted in.
- Runs (R): The number of runs scored.
- Highest score (HS/Best): The highest score ever made by the batsman.
- Batting average (Ave): The total number of runs divided by the total number of innings in which the batsman was out. Ave = Runs/[I – NO] (also Avge or Avg.)
- Centuries (100): The number of innings in which the batsman scored one hundred runs or more.
- Half-centuries (50): The number of innings in which the batsman scored fifty to ninety-nine runs (centuries do not count as half-centuries as well).
- Balls faced (BF): The total number of balls received, including no balls but not including wides.
- Strike rate (SR): The number of runs scored per 100 balls faced. (SR = [100 * Runs]/BF)
- Run rate (RR): Is the number of runs a batsman (or the batting side) scores in an over of six balls.
- Overs (O): The number of overs bowled.
- Balls (B): The number of balls bowled. Overs is more traditional, but balls is a more useful statistic because the number of balls per over has varied historically.
- Maiden overs (M): The number of maiden overs (overs in which the bowler conceded zero runs) bowled.
- Runs (R): The number of runs conceded.
- Wickets (W): The number of wickets taken.
- No balls (Nb): The number of no balls bowled.
- Wides (Wd): The number of wides bowled.
- Bowling average (Ave): The average number of runs conceded per wicket. (Ave = Runs/W)
- Strike rate (SR): The average number of balls bowled per wicket. (SR = Balls/W)
- Economy rate (Econ): The average number of runs conceded per over. (Econ = Runs/overs bowled).
Scorecards
See also: Scoring (cricket)
A match's statistics are summarised on a scorecard. Prior to the
popularisation of scorecards, most scoring was done by men sitting on
vantage points cuttings notches on tally sticks. The earliest known scorecards were printed in 1776 by Pratt, scorer to the Sevenoaks Vine Cricket Club, but it was many years before his invention was widely adopted.[55] Scorecards were printed and sold at Lord's for the first time in 1846.[56]The introduction of scoreboards revolutionised cricket by allowing spectators to keep track of the day's play. In 1848, Fred Lillywhite used a portable printing press at grounds to print updated scorecards. In 1858, the Kennington Oval introduced the first mobile scorebox, "a house on rollers with figures for telegraphing on each side". In 1881, the Melbourne Cricket Ground erected the first cricket scoreboard. The scoreboard, located at the western end of the ground, gave the batsman's name and method of dismissal.[55]





No comments:
Post a Comment